Grasping The Way Construction Design Elements Affect Overall Internet Connectivity in Apartment Complexes
Wiki Article
Wireless connectivity is now an essential resource in apartment complexes such as apartment complexes. However, numerous occupants encounter inconsistent wireless signal coverage due to conditions outside of router quality or internet service plans. A primary but often overlooked factor is the influence of structural components used in building design. Walls, floor systems, ceiling assemblies, and structural elements can either allow radio signals to pass through with minimal degradation or substantially weaken network performance. Recognizing how these components interact with radio frequency signals helps explain why wireless coverage differs so noticeably within the same building.
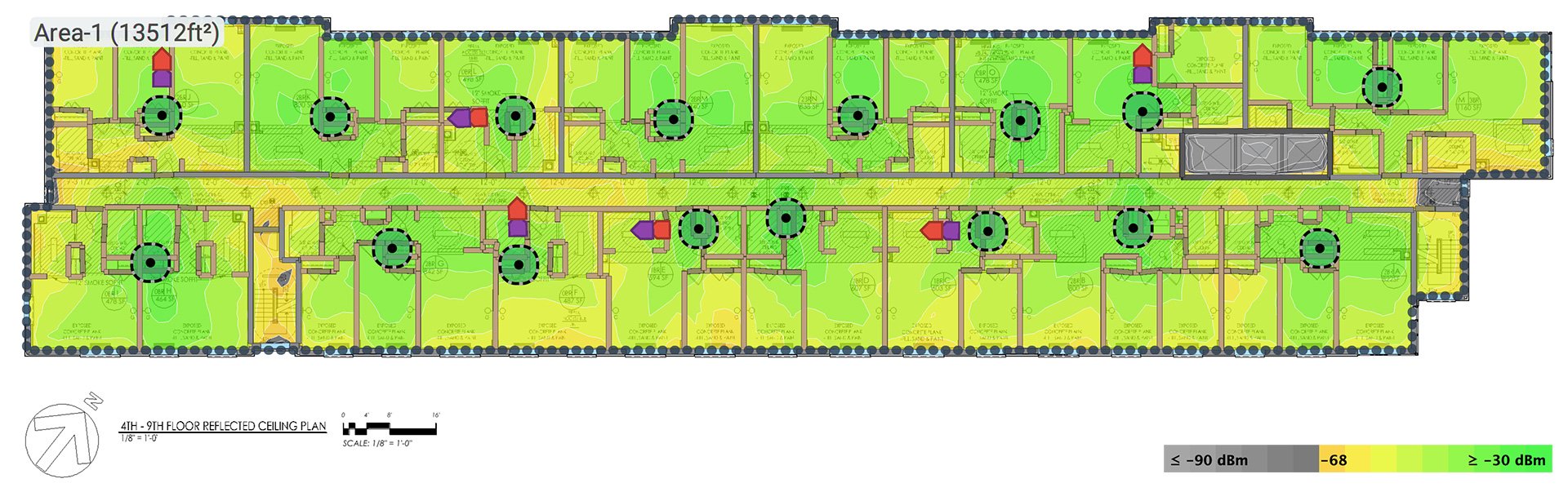
Wireless signals propagate as radio waves, which means their ability to move through a space depends on what they encounter. Materials like gypsum board and wood framing generally permit signals to travel with minimal signal loss, making them more supportive for stable connectivity. By comparison, high-density materials such as concrete, brick, and stone absorb and block signals more aggressively. Structural concrete, frequently used in multi-story housing, often contains steel rebar, which further disrupts signal propagation. This material mix can result in dead zones, reduced bandwidth, and unreliable go right here network stability across individual apartments.
Metal-based materials have an especially strong influence on wireless signal degradation. Steel framing, steel doors, lift shafts, and even reflective insulation can deflect and scatter radio frequencies. These reflections create signal distortion that degrade connection stability and limit data throughput. Additionally, high-efficiency construction materials designed for thermal insulation, such as low-emissivity glass or high-density insulation, can unexpectedly block wireless frequencies. While these solutions enhance energy performance, they often make it MDU internet for apartment complexes more difficult for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate interior spaces or levels.
Flooring and ceiling assemblies also play a role in vertical signal distribution within multi-level apartment complexes. Heavy structural slabs between floors can significantly limit signal penetration, making it challenging for a single wireless router to serve multiple floors. Tile flooring, stone finishes, and dense subfloor materials also contribute to attenuation. As a result, occupants on different floors may notice varying degrees of internet connectivity strength, even when operating identical wireless hardware. This challenge is particularly common in older buildings that were not planned with modern network infrastructure in mind.
To address these limitations, building managers and occupants often rely on connectivity solutions rather than structural changes. Mesh networks, wireless access points, and strategic router positioning help overcome coverage issues caused by construction components. Understanding how construction materials influence Wi-Fi performance allows for more efficient network planning and troubleshooting. In shared residential buildings, acknowledging the relationship between building materials and wireless signal quality is a key step toward ensuring consistent, stable connectivity for all occupants.